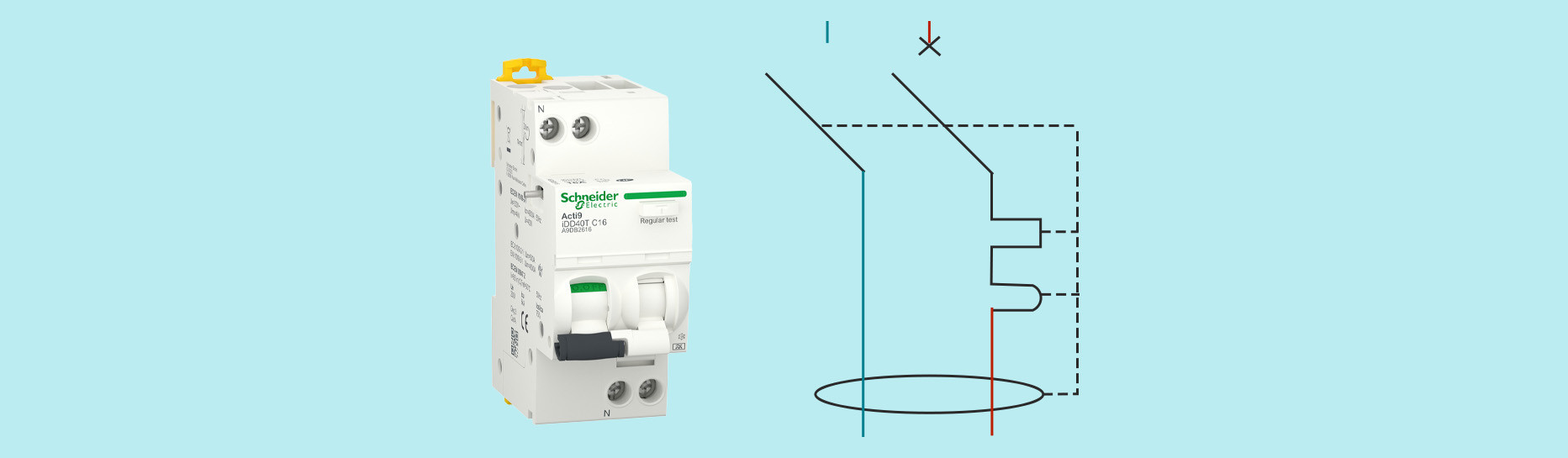
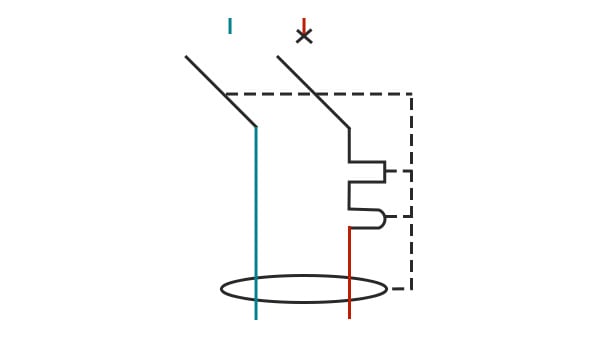
Understanding electrical symbols is a fundamental requirement for any professional or individual working with electricity. The differential circuit breaker symbol plays a central role in electrical installation diagrams. This standardized graphic representation makes it easier to read plans and ensures optimal safety.
What is a Differential Circuit Breaker?
A differential circuit breaker combines residual current protection and magnetothermal protection in a single modular device. This equipment detects current leaks to ground while providing protection against overloads. Its main function is to continuously monitor the difference between incoming and outgoing current.
This continuous monitoring allows any anomaly in the electrical installation to be detected instantly. The component reacts as soon as a current leak exceeds the programmed sensitivity threshold. The device then opens the circuit to protect both people and equipment.
The operating principle is based on comparing the currents flowing through the conductors. A differential transformer continuously measures this current difference. When the balance is disrupted, the protection device automatically triggers the cutoff.
Types of Differential Circuit Breakers
Electrical standards define several types of differential circuit breakers according to their specific applications. The AC type only detects alternating leakage currents to ground. This standard version is suitable for lighting circuits and conventional electrical outlets.
Type A extends detection to pulsed and alternating direct currents. This technology is essential for equipment that generates direct current, such as washing machines. Cooktops and electric vehicles also require this enhanced protection.
Type Asi offers superior immunity to false tripping. This super-immunized version is suitable for installations that are sensitive to power interruptions. Computer circuits and electronic lighting systems benefit from this increased stability.
Type B is suitable for three-phase installations with complex differential current risks. Variable frequency drives and inverters require this specialized protection. This advanced technology detects all types of fault currents.
Symbols Associated with Differential Circuit Breakers
The key components of the symbol include:
- A rectangle: main body of the device
- Diagonal contacts: cutoff function
- Circle with wavy line: differential protection
- Stylized coil: magnetic protection (against short circuits)
- Serrated rectangle: thermal protection (against overloads)
The graphical representation of the differential circuit breaker combines several distinct symbolic elements. The main rectangle represents the device body in the electrical diagram. The moving contacts are shown by diagonal lines indicating the cutoff function.
The differential symbol is characterized by a circle crossed by a wavy line. This universal representation immediately identifies the differential protection function. The toroidal transformer sometimes appears as a circle with a schematic winding.
Each terminal corresponds to a specific conductor in the electrical installation. The phase and neutral conductors have their own dedicated positions.
The magnetothermal release is identified by specific additional symbols. A serrated rectangle represents thermal protection against prolonged overloads. A schematic coil symbolizes magnetic protection against short circuits.
Standardization of Electrical Symbols
The only difference between the symbol for a residual current circuit breaker and that for a differential circuit breaker is the small circles at the terminals for the differential circuit breaker.
The IEC 60617 standard internationally standardizes all symbols used in electrical diagrams. This harmonization ensures universal understanding of the graphic representations. Differential circuit breaker symbols strictly comply with these international codes.
Each element of the differential circuit breaker symbol has a specific, codified meaning. The position of the contacts indicates the normal state of the device in the installation. The relative dimensions comply with the proportions defined by the standards.
Color coding can provide additional information on certain specialized electrical diagrams. However, the shape remains the primary element for identifying the electrical component. This approach ensures readability even on black and white documents.
Reading and Interpreting Electrical Diagrams
Correct interpretation of diagrams requires thorough knowledge of electrical symbols. The differential circuit breaker symbol fits into an overall representation logic. Its position in the diagram indicates its role in the electrical architecture.
Reading an electrical panel begins with identifying the main supply. The various outputs are then distributed according to clear functional logic. Each circuit has its own specific protection adapted to the equipment it supplies.
Electrical diagrams use different views depending on their technical purpose. The single-line diagram simplifies the representation for an overview. The multi-line diagram details all the connections for practical implementation.
Understanding the symbols greatly facilitates work on electrical installations. A trained professional can immediately identify the protections present in a panel. This speed of analysis improves the efficiency and safety of interventions.
Training and Application of Electrical Symbols
Mastery of electrical symbols is acquired through theoretical and practical training. Technical schools incorporate this knowledge into their electrical engineering curricula. Knowledge is regularly updated in line with changes in standards.
The practical application of symbols begins at the design stage of electrical installations. Design offices use specialized software that incorporates standardized symbols. This computerized approach ensures consistency and compliance in representations.
Electricians use these symbols daily to interpret installation diagrams. The ability to read plans quickly is essential for efficient maintenance work. Good knowledge of symbols significantly reduces the risk of error.
Continuing education keeps pace with developments in electrical technologies and standards. New symbols appear with technological innovation in the electrical field. This constant adaptation ensures that standardized symbols remain relevant.
Expertise in reading symbols distinguishes qualified professionals from amateurs. This technical skill ensures the safety of both people and installations. Investment in this training quickly pays dividends for any professional.
The symbols used for differential circuit breakers evolve with technological innovations in the sector. Manufacturers such as Schneider Electric and Legrand offer increasingly efficient solutions. These developments are sometimes accompanied by new, adapted symbols.
Discover our selection of professional differential circuit breakers at One-Elec. Our experts will advise you on choosing the right equipment for your electrical installations. Take advantage of our competitive prices and permanent stock availability for your projects.